HellermannTyton has developed a range of RFID cable ties, accessories and RFID readers to make your RFID tracking and identification processes more efficient. The variety of applications makes RFID technology so unique:
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a smart solution for identification, serialisation and tracking of products in several areas and industries. Watch this video to find out how RFID works and how it can be applied for industry purposes:
 T50RFIDCLA
111-01638
T50RFIDCLA
111-01638 T50RFIDCHA
111-01639
T50RFIDCHA
111-01639 T50RFIDCHA
111-01591
T50RFIDCHA
111-01591 T50RFIDCHA
111-01673
T50RFIDCHA
111-01673 MCTRFIDCLA
111-01976
MCTRFIDCLA
111-01976 MCTRFIDCHA
111-01676
MCTRFIDCHA
111-01676 MBT8HFCRFID
156-01167
MBT8HFCRFID
156-01167 TAG110x13T1UHFM
556-00841
TAG110x13T1UHFM
556-00841 TAG54x24T1UHFM
556-00844
TAG54x24T1UHFM
556-00844 RFID FLEXTAG 83x25
556-00803
RFID FLEXTAG 83x25
556-00803 RFID HARDTAG DISC
556-00809
RFID HARDTAG DISC
556-00809 HardTag Solid 60x18
556-00852
HardTag Solid 60x18
556-00852 RFID HARDTAG SOLID 105x35
556-00811
RFID HARDTAG SOLID 105x35
556-00811Several tasks are combined: the cable tie acts as an information carrier, product label and cable fastening – all at the same time
Learn more about the benefits of HellermannTyton RFID solutions here in this video:
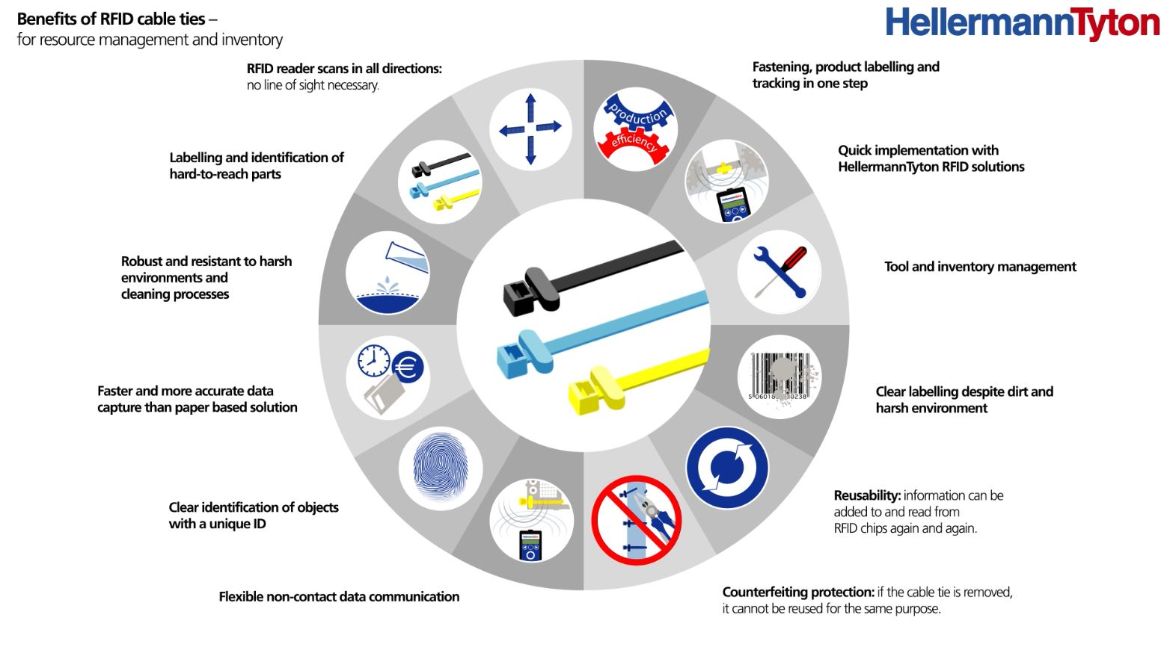
RFID tracking is used in many industries. The combination of material, transponder, reading distance and surroundings decides on the use of it.

A good example is tracking products for asset management, where RFID systems simplify the identification and management of valuable tools or equipment substantially. For this, the product to be labelled just needs to be fitted with one of HellermannTyton RFID cable ties that has been programmed with a unique code.
You can either link the pre-programmed code with a database or add specific code requirements according to your database needs.
Read one example for RFID tracking of our case studies on our HellermannTyton Blog.
The fact that each component is traceable also benefits the goods receipt. Costs become more transparent, processes along the value stream can be optimized. Product counterfeits are easier to identify. The use of RFID cables makes them completely impossible: once a cable connector is cut off, it can not be reused - because each RFID chip has a unique ID. The RFID cable ties guarantee the authenticity of the information stored on them.

Take an offshore wind farm as another example for RFID tracking. Engineers need to take commonly used valuable equipment with them on site to fulfill repair or maintenance tasks.
In order to manage the inventory and/or e.g. identify the location of the equipment it can be fitted with an RFID cable tie. The programmed information can be linked to a database that serves as an information and management tool for an easy way of tracking the tools.
With the help of NFC technology (near-field communication) the engineer can communicate with the RFID tie by using an app on their tablet PCs. This way it is e.g. possible to check out the equipment prior to the use and check it back in after finishing the job. The big benefit resulting from such a system is the permanent control, which have both users and administrators of these assets.
Read more about this example for RFID tracking in our RFID blog article.

Where conditions in the production facility are extreme, such as heat, dirt and liquids, RFID cable ties made of different materials are the ideal solution.
For example hydraulic service which carries out repairs to hoses. Extreme conditions come together here. A mixture of hydraulic oil, screw solution and dirt blurred the conventional product labelling until it was indecipherable. This was very problematic for the service staff. They could no longer identify which type of hose they were dealing with. What is the maximum pressure load of the hose? When was the hose made and installed? Who worked on it last?
The solution for the service company was to use HellermannTyton RFID cable ties made of metal, which are not affected by oil or heat.

There are numerous other fields of application for RFID tracking, like crane construction. One example: Previous product labels were difficult to access and were no longer readable because several layers of paint were applied at the customer’s request. Now using HellermannTyton RFID cable ties for identification the information remains permanently readable as the chip is housed in and can withstand harsh environments or layers of paint.
Read more in our RFID blog article.

Processes are also simplified and optimised in the case of traceability of components. For example, in the case of defects, recalls or the monitoring of maintenance intervals.
Or for product labelling in general, such as when installing elements in automobiles.
Here, the RFID cable tie also acts as a security measure which is more reliable and involves less effort than conventional labelling solutions. If the cable tie is ever cut off it cannot be reused.
The authenticity of the information on the RFID cable tie as product labelling is therefore guaranteed. This means, for example, you can very accurately trace which employee installed which component with which properties in which factory on which day.
RFID tracking for inventory management: All HellermannTyton RFID products can be used for securing, serialisation, tracking and identification of products in the areas of resource management, electrical inspection, inventory, distribution and rental services as well as for easy management of maintenance and repair routines.

RFID cable ties provide an innovative solution for clear and rapid product RFID tracking.
The nylon cable ties are equipped with an RFID transponder and therefore combine the numerous advantages of regular cable ties with RFID technology.
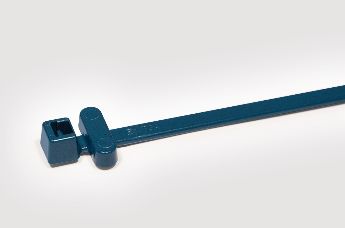
Metal content RFID cable ties are made with a percentage of a metallic trace element (magnet/X-Ray) and have been especially developed for industries where the potential for contamination is a problem.
The ties can be used for securing, serialisation, tracking and identification of products e. g. in the food processing, chemical or pharmaceutical industry to support quality control effort.

Stainless steel RFID cable ties are fitted with a slide-on carrier for a high frequency (HF) or an ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID transponder.
These ties are ideal for product identification in all areas of harsh environment where high tensile strength and durability is of importance.

The HEXTAG made from PA66 is equipped with transponder of HF frequency.
The central hole allows a simple mounting in applications where a RFID cable tie solution is not suitable.
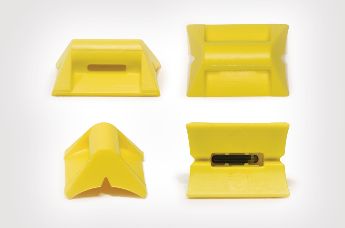
The CRADLE, made of TPU and equipped with a HF transponder can be used on standard HellermannTyton cable ties.

The HS9 handheld RFID readers are designed to read LF transponders and read/write to HF transponders fitted to HellermannTyton RFID cable ties and accessories.
The HS9 reader is available for low frequency (LF, 125 kHz, read-only) and for high-frequency (HF, 13.56 MHz, read & write) transponders.

The RFID-DT22 desktop reader for stationary use has been designed to read and write from/to high frequency (HF 13.56 MHz) transponders fitted to HellermannTyton RFID cable ties and accessories.
The readers act as an interface between the RFID transponder and computer systems or databases. Radio waves transmit the data from the RFID transponder to the reader, so that contactless reading and/or writing of information is possible.
RFID, or Radio-Frequency Identification, is a technology that allows for the wireless identification and tracking of objects using radio waves. It consists of three main components: RFID transponders or tags, RFID readers, and a backend database or software system. The idea of how to track RFID tags is very simple: the tag contains a microchip holding information about the tagged object as well as an antenna enabling the tag to communicate with a reader. The reader captures the signal from the tag and passes it on to a computer system or software where it is processed.
![]()
Barcodes and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) are both technologies used for identifying and tracking items, but they differ in their underlying applications.
RFID uses radio frequency signals to identify and track objects. RFID tags can be read even when not directly visible to the reader. They can also store more information than barcodes and since multiple tags can be read simultaneously, RFID is more efficient for tracking large quantities. Also, RFID tags are more robust than barcodes.
RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) technology can potentially be hacked, like any other technology. However, not all RFID systems are equally vulnerable. The feasibility and complexity of hacking RFID systems depend on various factors, including the specific type of RFID technology being used, the security measures in place, and the attacker's skill level. Responsible implementation of security measures can greatly mitigate the risks associated with RFID hacking.
RFID tags can be reused and recycled. Most importantly, the content saved on the tags can be overwritten and the RFID tags can therefore be used repeatedly. Another key advantage of RFID lies in the use cases. For example, RFID tags can be used to track waste bins. When processing the waste, type, weight, and environmental impact can be tracked. This information could be used to calculate the charge for that bin, thus encouraging the bin owner to change their behaviour to produce less impactful waste.
RFID tags can be reused and recycled. Most importantly, the content saved on the tags can be overwritten and the RFID tags can therefore be used repeatedly. Another key advantage of RFID lies in the use cases. For example, RFID tags can be used to track waste bins. When processing the waste, type, weight, and environmental impact can be tracked. This information could be used to calculate the charge for that bin, thus encouraging the bin owner to change their behaviour to produce less impactful waste.